The Rise of AI in Governance: Transforming Public Administration for the Digital Age
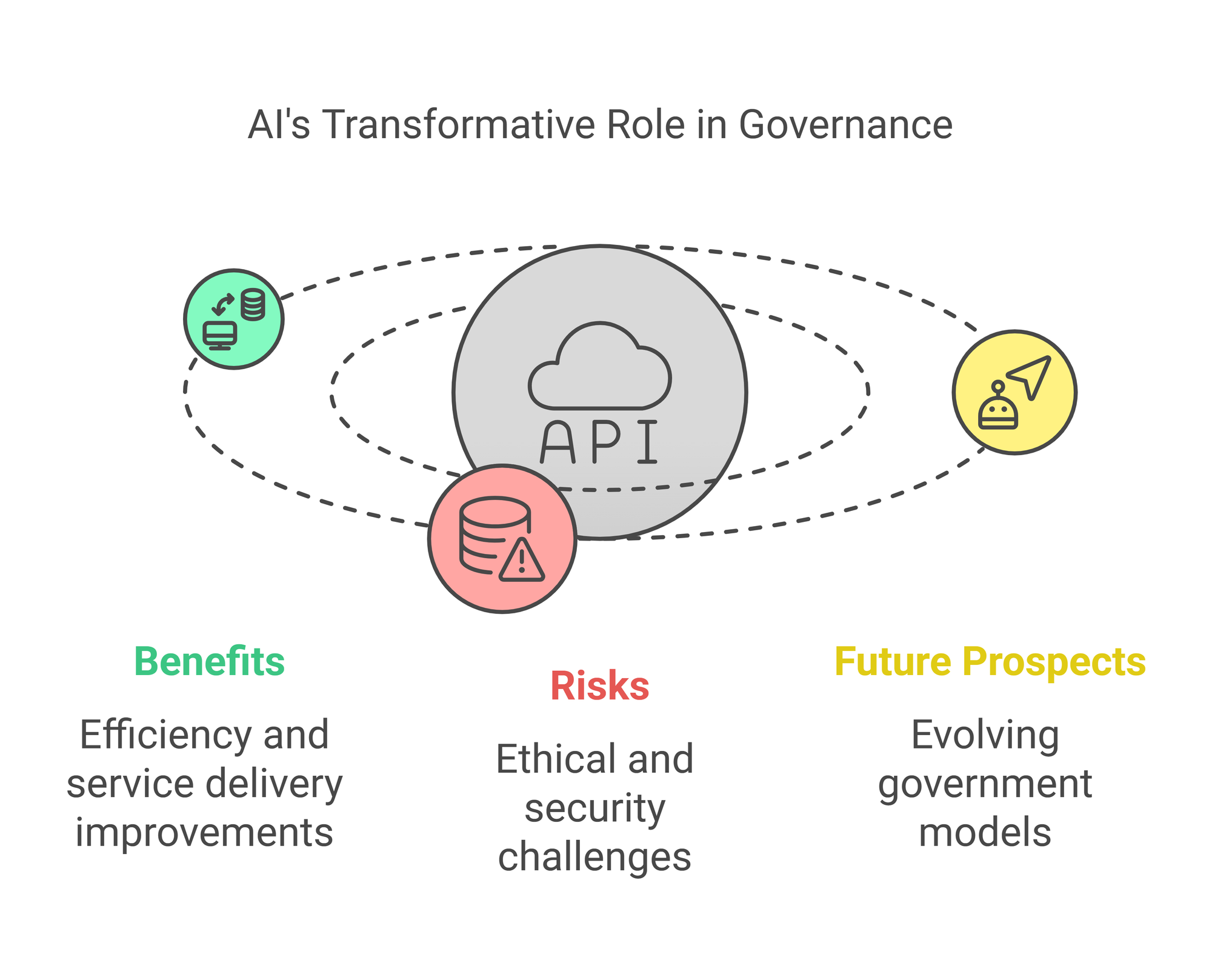
AI is transforming governance by optimizing public services, policymaking, and urban planning. It enhances transportation, predicts infrastructure needs, and improves emergency response. However, ethical concerns and data security challenges must be addressed for responsible implementation.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries worldwide, and governance is no exception. The integration of Generative AI (GenAI) tools, including advanced language models and automation technologies, is reshaping how governments operate. From policymaking to public service delivery, AI-powered solutions are unlocking efficiencies, streamlining bureaucratic processes, and enhancing citizen interactions. However, these transformations come with challenges, including ethical considerations, data security risks, and regulatory hurdles. This article delves into the evolving role of AI in governance, its potential benefits, risks, and the future of AI-driven government models.
The Evolution of AI in Governance
Traditional Governance vs. AI-Augmented Administration
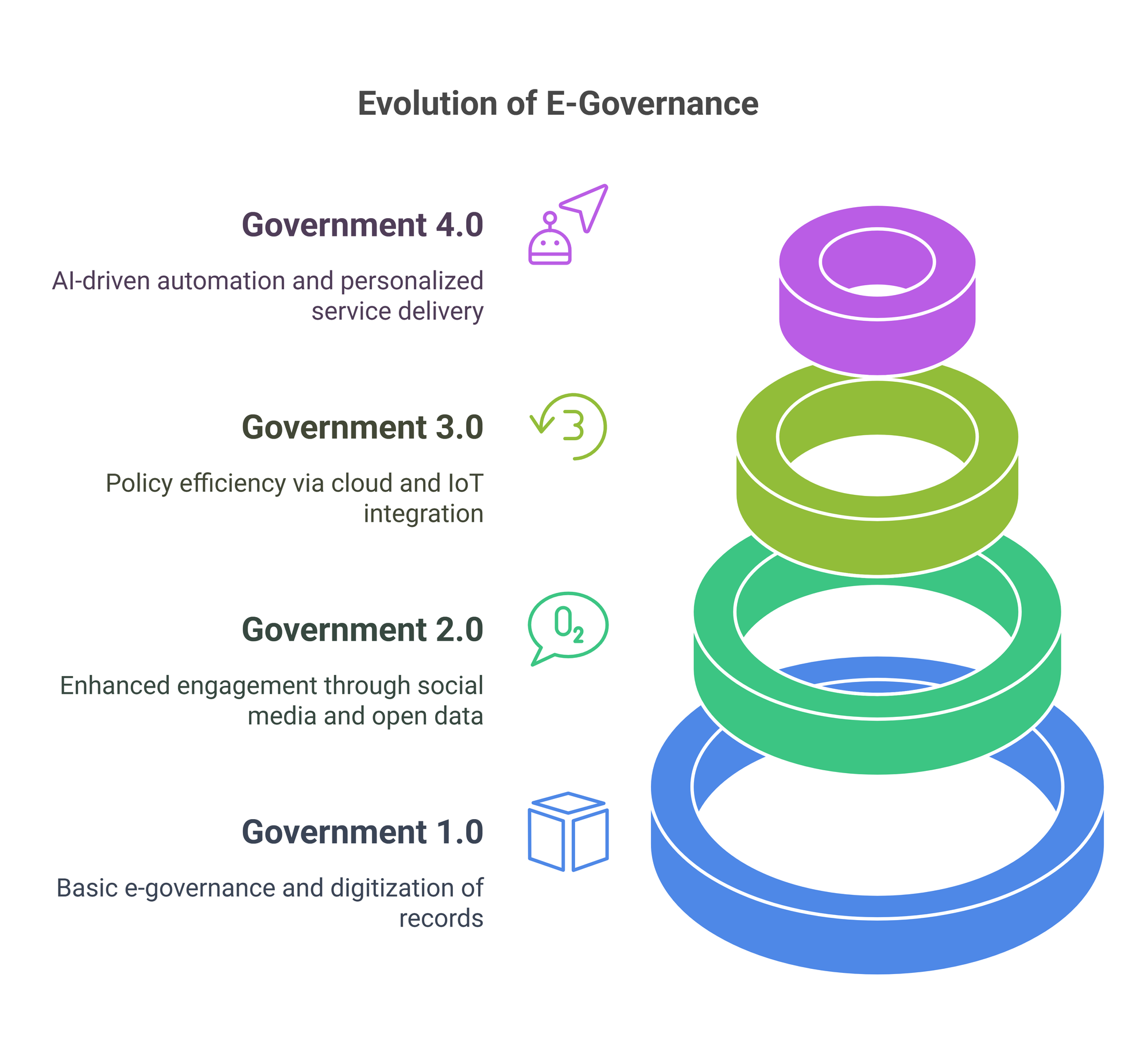
Governments have historically relied on manual processes, human expertise, and traditional decision-making frameworks. However, with the advent of digital technologies, governance has evolved significantly:
- Government 1.0: The introduction of the internet enabled online services, allowing governments to digitize public records and provide basic e-governance functions.
- Government 2.0: Social media and open data policies enhanced citizen engagement and transparency in decision-making processes.
- Government 3.0: Cloud computing, big data analytics, and IoT integration led to improved policy efficiency and smart city initiatives.
- Government 4.0: The current phase, powered by AI, is characterized by intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized service delivery.
Key Areas of AI Implementation in Government
1. Enhancing Public Service Delivery
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are improving how citizens interact with government agencies. These tools provide real-time support, automate document processing, and reduce the need for human intervention in routine administrative tasks. Examples include:
- AI-powered tax assistants for quick tax calculations and filing assistance.
- Automated permit and license applications, reducing wait times for approvals.
- AI-enhanced healthcare portals that provide personalized health recommendations based on user input.
2. AI in Policy Development and Decision-Making
AI’s ability to process vast datasets and identify trends enables policymakers to make informed decisions. AI can:
- Analyze public sentiments through social media monitoring.
- Predict the outcomes of policy changes by modeling different scenarios.
- Provide real-time feedback on the impact of new laws and regulations.
3. Strengthening Governance and Accountability
AI can play a pivotal role in promoting transparency and reducing corruption. Governments can utilize AI to:
- Detect financial irregularities in public spending.
- Monitor procurement processes to prevent fraudulent activities.
- Generate public reports and summaries for greater citizen oversight.
4. AI for Smart Cities and Infrastructure Planning
Urban planning is becoming more data-driven, with AI analyzing traffic patterns, population growth, and environmental impact assessments. AI-driven tools assist in:
- Optimizing public transportation networks.
- Predicting infrastructure maintenance needs.
- Enhancing emergency response systems by analyzing past disaster patterns.
5. AI in Law Enforcement and Public Safety
AI is transforming security and law enforcement by:
- Analyzing crime data to predict high-risk areas.
- Enhancing surveillance systems with facial recognition and anomaly detection.
- Automating forensic investigations by analyzing legal documents and evidence.
Potential Risks and Challenges of AI in Governance
While AI offers numerous benefits, its integration into governance comes with several challenges that must be addressed:
1. Ethical and Bias Concerns
AI systems learn from historical data, which may contain biases. If not properly managed, AI could reinforce existing inequalities, leading to unfair decision-making in areas such as law enforcement, hiring, and social welfare programs.
2. Data Privacy and Security Issues
Governments collect massive amounts of citizen data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Ensuring secure AI systems is crucial to preventing data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
3. Dependence on AI and Job Displacement
Automation reduces the need for human labor in certain administrative roles. Governments must plan for workforce transitions by investing in AI literacy programs and creating new job opportunities in AI governance.
4. Algorithmic Transparency and Accountability
AI decisions must be explainable and transparent. If an AI system denies a citizen access to a government service, there must be a clear explanation and an appeals process in place to ensure fairness.
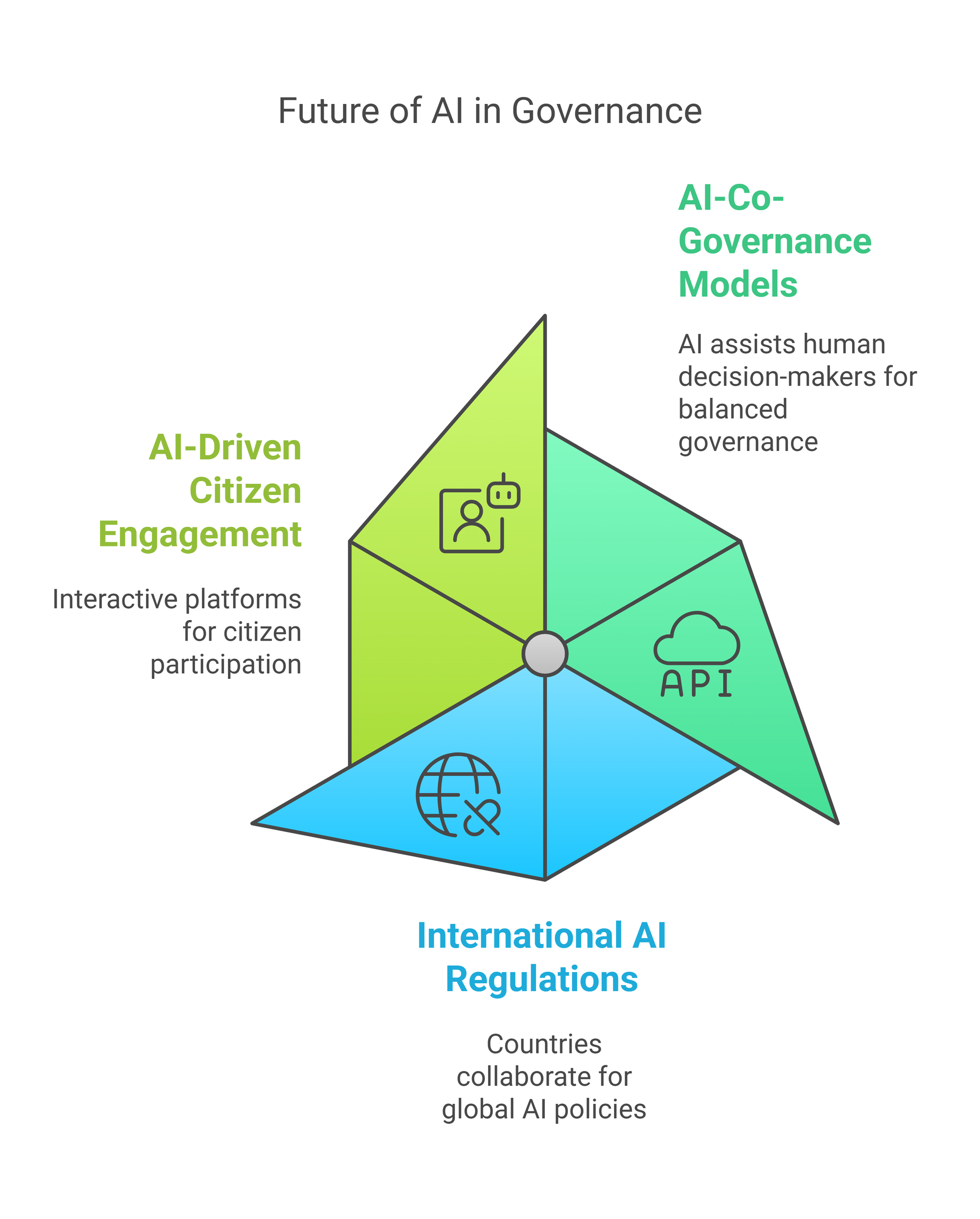
Future Prospects: Towards AI-Governed Societies
As AI continues to advance, we can expect:
- AI-Co-Governance Models: AI will assist human decision-makers rather than replace them, ensuring a balanced approach to governance.
- International AI Regulations: Countries will collaborate to establish global AI policies that promote ethical AI use.
- AI-Driven Citizen Engagement: More interactive platforms will enable citizens to directly participate in governance through AI-powered consultations and real-time feedback mechanisms.
Conclusion
The rise of AI in governance represents a paradigm shift in public administration. By leveraging AI’s capabilities, governments can enhance efficiency, transparency, and citizen engagement. However, careful implementation is required to mitigate risks and ensure ethical AI governance. As we move towards AI-augmented government models, continuous dialogue among policymakers, technologists, and citizens will be crucial in shaping a future that balances innovation with responsibility.




